[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5- a ]pyrimidine Phosphodiesterase 2A Inhibitors: Structure and Free-Energy Perturbation-Guided Exploration.
Tresadern, G., Velter, I., Trabanco, A.A., Van den Keybus, F., Macdonald, G.J., Somers, M.V.F., Vanhoof, G., Leonard, P.M., Lamers, M.B.A.C., Van Roosbroeck, Y.E.M., Buijnsters, P.J.J.A.(2020) J Med Chem 63: 12887-12910
- PubMed: 33105987
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01272
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ZND, 6ZQZ - PubMed Abstract:
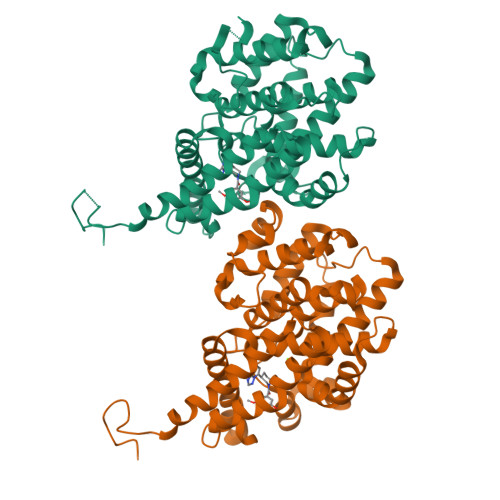
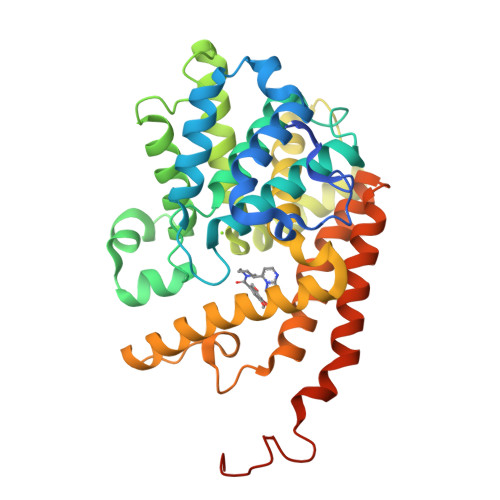
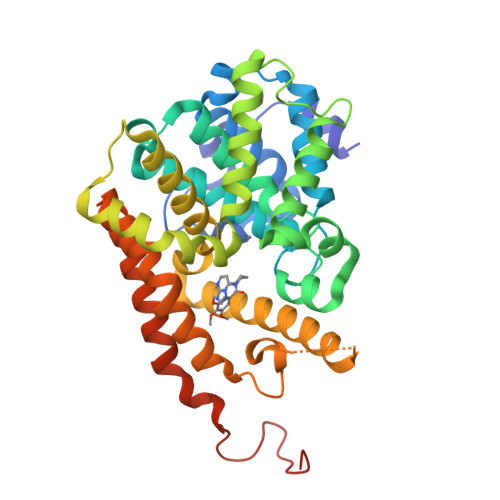
We describe the hit-to-lead exploration of a [1,2,4]triazolo[1,5- a ]pyrimidine phosphodiesterase 2A (PDE2A) inhibitor arising from high-throughput screening. X-ray crystallography enabled structure-guided design, leading to the identification of preferred substructural components. Further rounds of optimization used relative binding free-energy calculations to prioritize different substituents from the large accessible chemical space. The free-energy perturbation (FEP) calculations were performed for 265 putative PDE2A inhibitors, and 100 compounds were synthesized representing a relatively large prospective application providing unexpectedly active molecules with IC 50 's from 2340 to 0.89 nM. Lead compound 46 originating from the FEP calculations showed PDE2A inhibition IC 50 of 1.3 ± 0.39 nM, ∼100-fold selectivity versus other PDE enzymes, clean cytochrome P450 profile, in vivo target occupancy, and promise for further lead optimization.
Organizational Affiliation:
Computational Chemistry, Janssen Pharmaceutica N. V., Turnhoutseweg 30, B-2340 Beerse, Belgium.